Egg Freezing (Oocyte Cryopreservation)

Egg freezing, medically known as oocyte cryopreservation, is a method of fertility preservation that allows women to store their eggs (oocytes) at a younger and healthier stage of life for use in the future.
This technique is especially valuable for women who wish to delay pregnancy due to personal, medical, or professional reasons, or for those who may face treatments (such as chemotherapy or surgery) that could damage their fertility.
How Egg Freezing Works:
Ovarian Stimulation:
The woman receives hormone injections for about 10–12 days to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple mature eggs instead of just one.
Egg Retrieval:
When the eggs are ready, they are collected from the ovaries through a minor outpatient procedure under light anesthesia.
Freezing (Cryopreservation):
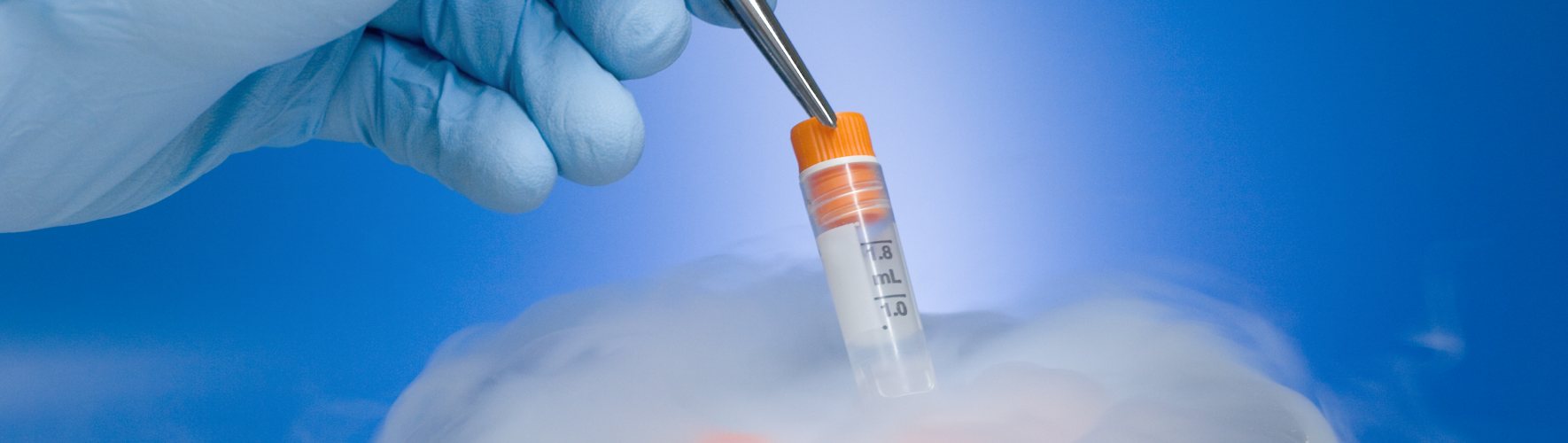
The retrieved eggs are frozen using a rapid freezing technique called vitrification, which prevents ice crystal formation and preserves the egg’s quality.
Storage:
The frozen eggs are safely stored in liquid nitrogen at –196°C, where they can remain viable for many years.
Future Use:
When the woman decides to become pregnant, the eggs are thawed, fertilized with sperm through IVF (In Vitro Fertilization), and the resulting embryos are transferred into the uterus.
Who Can Benefit from Egg Freezing?
Women who want to delay motherhood for personal or career reasons
Cancer patients before undergoing chemotherapy or radiotherapy
Women with family history of early menopause
Patients with endometriosis or other conditions that may affect ovarian reserve
Individuals undergoing gender transition who want to preserve fertility
Advantages of Egg Freezing:
Maintains the possibility of biological motherhood in the future
Provides emotional and psychological reassurance
Prevents age-related decline in egg quality
Enables family planning flexibility
In Summary:
Egg freezing is a safe, proven, and empowering fertility preservation method that gives women greater control over their reproductive future. With advances in vitrification technology, the survival and pregnancy rates from frozen eggs are now comparable to those of fresh eggs.
Sperm Freezing (Semen Cryopreservation)

Sperm freezing, or semen cryopreservation, is a medical procedure used to collect, freeze, and store sperm for future use. This method allows men to preserve their fertility in advance, especially if there is a risk that their ability to produce healthy sperm might decline over time or be affected by medical treatments.
It is a simple, safe, and highly effective technique widely used in fertility preservation and assisted reproductive treatments such as IUI and IVF.
How Sperm Freezing Works:
Sperm Collection:
A semen sample is usually collected through masturbation in a private room at the fertility center. In some cases, sperm may be obtained through minor surgical procedures (e.g., TESA or TESE) if ejaculation is not possible.
Semen Analysis:
The sample is examined in the lab to evaluate sperm count, motility, and morphology (shape and movement).
Processing and Freezing:
The healthiest sperm are separated and mixed with a special protective solution (cryoprotectant) to prevent damage during freezing. The sample is then rapidly frozen using liquid nitrogen at –196°C.
Storage:
Frozen sperm samples are stored in specialized tanks and can remain viable for many years without losing fertilizing ability.
Future Use:
When needed, the sample is thawed and used for IUI (Intrauterine Insemination) or IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) procedures.
Who Can Benefit from Sperm Freezing?
Cancer patients before chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or surgery
Men planning vasectomy but wanting the option of future fertility
Those with declining sperm quality due to age or medical conditions
Men with high-risk occupations (e.g., military, hazardous environments)
Individuals undergoing gender transition treatments
Couples undergoing assisted reproduction who wish to store extra sperm samples
Advantages of Sperm Freezing:
Simple, fast, and non-invasive procedure
Long-term fertility preservation
Maintains the possibility of biological fatherhood
Ensures sperm availability even during medical treatment or absence
High post-thaw survival and fertilization rates
In Summary:
Sperm freezing is a safe and reliable method for protecting male fertility. With advances in cryopreservation technology, frozen sperm can remain effective for decades, offering men the opportunity to plan fatherhood whenever the time is right.
Embryo Freezing (Embryo Cryopreservation)
Gynecological surgery refers to surgical procedures performed on the female reproductive system, including the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix, and vagina. These procedures are used to treat diseases, correct anatomical problems, relieve pain, enhance fertility, or prevent cancer.
Common Types of Gynecological Surgery:
Hysterectomy:
Removal of the uterus, either total or partial
Indicated for fibroids, heavy menstrual bleeding, chronic pain, or cancer
Ovarian Surgery:
Removal of cysts, tumors, or treatment of endometriosis
May involve oophorectomy (removal of the ovary) if necessary
Myomectomy:
Surgical removal of uterine fibroids while preserving the uterus
Recommended for women who wish to maintain fertility
Tubal Surgery:
Repair or removal of fallopian tubes
Treats blocked tubes, ectopic pregnancy, or tubal sterilization reversal
Cervical Procedures:
LEEP or conization to remove precancerous cervical tissue
Used for cervical dysplasia or early-stage cervical cancer
Minimally Invasive (Laparoscopic) Surgery:
Uses small incisions and a camera for procedures like endometriosis removal, cystectomy, or tubal surgery
Benefits include less pain, shorter recovery, and minimal scarring
Vaginal Surgery:
Corrects pelvic organ prolapse, urinary incontinence, or vaginal reconstruction
Indications for Gynecological Surgery:
Persistent pelvic pain or abnormal uterine bleeding
Reproductive disorders affecting fertility
Cancerous or precancerous conditions of the reproductive organs
Large fibroids or ovarian cysts causing symptoms
Congenital reproductive abnormalities
Benefits of Gynecological Surgery:
Relief from pain and discomfort
Correction of anatomical or functional problems
Treatment or prevention of gynecologic cancers
Improvement in fertility and reproductive health
Use of minimally invasive techniques for faster recovery